Trading Fx in itself is a pretty straightforward business. However, the overall interaction between the various participating groups adds up to a complex affair. The big question is – who is the forex market maker?
To answer the question, first, we need to understand these players. The group of Fx participants is a big bunch. You see, the Forex market breaks down into a large number of speculators of varying sizes and with very different objectives.
You have Intraday traders, Swing traders, Long term Investors. And, if you add the HFT machines with their scalping methodologies into the mix, you can see how this, quickly becomes very complex.
The FX Marketplace structure in a nutshell
At the very top of the Fx pyramid, there is an Interbank. This is the level where major financial Institutions are exchanging their currencies. Imagine this being a wholesale place for buying and selling the currencies. It is here, where we can witness the true power of the forex market maker.
Each Bank has a dedicated market-maker that is curating each major currency pair. It provides quotes at which the bank is willing to buy and sell currencies from their fellow bank partners in the Interbank network. Therefore, without a shadow of a doubt, we can say that the Institutions that are on the Interbank level are the primary market-makers of the FX arena.
Some of the largest market makers in forex include:
- JPMorgan Chase
- Deutsche Bank
- UBS
- Citigroup
- Barclays
- Goldman Sachs
- HSBC
- Morgan Stanley
- Credit Suisse
- BNP Paribas
These institutions often play a significant role in setting currency exchange rates and market trends due to their large trading volumes and extensive networks.
One of the sophistications of the Interbank marketplace, and maybe one of the important factors, is the credit relationships that the major banks have with each other. The banks buy and sell currencies between each other with this credit-worthy approach.
Not to mention, the deal sizes on the Interbank level are typically very large. Definitely, out of reach of retail trader’s pocket. These combined nuances prevent, or should I say filter, most participants from directly accessing the Interbank market. In essence, the Interbank is self-regulating itself with the above-mentioned factors.

Indeed, there was a time period, not so long ago, give or take, twenty years ago when the Fx marketplace was strictly the domain of large banking companies and genuinely well-established financial Institutions.
Thanks to the technological and data processing revolution, that all has changed! The rise of Retail FX was inevitable.
Nowadays, everybody can access the Forex market easily and compete with large banks for a share of Fx profits. This is done through the retail Fx brokers. Usually, it is either an ECN or an STP broker that plays the role of an intermediary between the “average Joe” and the Interbank. Later on, we’ll be discussing the difference between the market-makers, but for now, let’s focus on the role of the Forex market maker.
Market Maker’s Role
The primary role of the market-maker is to do what its name implies – to make the market!
A market maker sets two-way prices in a certain currency pair in order to make a market.
Essentially, a forex market maker does a couple of things:
Sets two-way prices (bid/offer) prices in a particular currency pair.
Commits to accepting orders at the current market prices.
Since the Fx market maker is a counterparty to a trade, it takes the resulting exposure from the order-flow on onto their own order book. What this means, they are not matching the trade with another party in the way that an ECN or an STP broker would. An Interbank market maker may choose to hedge his exposure with another bank if he can obtain a favorable rate.
How much of a risk they decide to take on or to take off the table, will be at their sole discretion.
Basically, they are the “800-pound gorillas” of the financial jungle.

Obviously, large banks see huge flows of foreign currency transactions from their daily operations. As a result, they’re able to achieve significant profit from just simply collecting the spread day, after day.
However, the Bank is not limited by this day-to-day activity of making the market and collecting the spread. A dealer bank may also choose to take a position in the Fx market if it decides to do so because it can see its order book across the board.
They can do this either, by making a trade with another member bank, or by quoting the currency accordingly in order to induce trades in a certain direction.
OK, If you think that making a market is an easy business, think twice…
Actually, bank dealers have to consider a number of factors before making their prices.
Here are just some of them:
– current volumes at the prevailing market rate
– current rates that are being offered elsewhere on the Interbank network
– the volume of the deal they are quoting
– their own exposure in the Market (the open positions they already have on their books)
– overall view on the future value of the currency pair
Obviously, there is a market-maker for each market: Stocks, Options, Bonds, and Futures. So how do these types of market-makers stack against each other? Let’s compare the two, Fx and Equities for example.
Right from the start, Equities are being traded on the exchanges, where trade information is publicly available. This means, that the true price and volume are available for speculators in these markets.
This is a big plus, where the FX dealings of large banks are considered a piece of proprietary information, and on top of that, there is no mandate for the info to be disclosed. The forex market maker is aware of large orders placed by financial Institutions before the rest of the participants. Hence, they are aware of the potential market-moving trades.
Essentially, this gives them an unfair advantage over the other market groups.
Benefits of Forex Market Maker
The difference between a Retail FX broker and a True Market Maker
A number of Retail firms are often times referred to as market-makers, however, in reality, they do not actually perform the root functions of a true Market Maker. Some Retail companies may operate successfully as a broker. Meaning, that they hedge their risk immediately with their liquidity providers. Others may take some of the risk onto their own books.
The key difference, they do not make their own prices as a true market maker. These Retail shops usually offer aggregated quotes for any particular pair. Simply put, they offer their clients the best bid/offer prices they have access to through the market-making partners. These partners are the large banks from the Interbank level, who operate as prime brokers for these firms.
The way the partners grant access to their liquidity is through the ECN – Electronic Communications Network.
An ECN software organizes bids and offers from larger banks, and financial institutions and puts them into an order book. Now, when you place a trade, the ECN will match your order against the very best price available. The ECN networks are operating at lightning speed. The orders are matched in milliseconds and the spreads are usually very competitive.
Also, there are STP – Straight Through Processing brokers as well. Despite the fact that ECN connects orders with those of other market participants as well as main liquidity providers, in the core they are very similar programs. The main difference, an ECN taps into a bigger pool of orders than a standard STP.
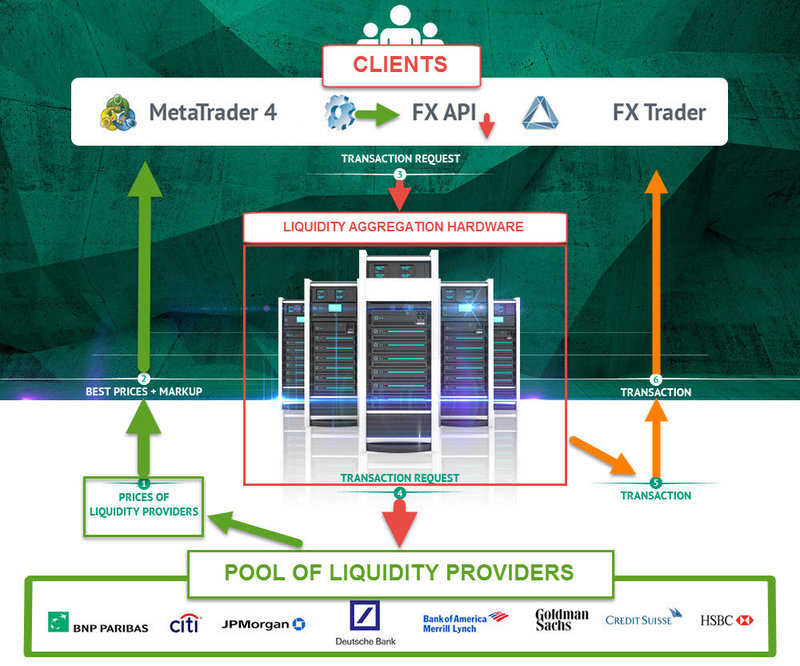
Now, there are long debates in the Retail Forex community, about whether it is best to use ECN and STP brokers over a true market-making Dealer Broker. The dealer broker – the one, that is taking the opposite side of your trades. To answer this question we need to step back and reflect upon what was going on during the Swiss National Bank debacle. Every Fx trader remembers that time period. Let’s not kid ourselves, it was a disastrous period for many of us…
On January 12, 2015, a financial tsunami ripped through the FX market, when the Swiss National Bank decided to unpeg its currency from the EURO. This caused the Swiss Franc to appreciate against the EURO by more than 30% in a matter of minutes.
“How is this relevant to the topic?” – you may ask…
Well, let’s put ourselves in the shoes of an STP Broker. What would happen in case of a lack of liquidity is as follows: you would accumulate orders in a matter of seconds, then as a Straight Through Processor you would want to transfer those orders to your liquidity partner, but guess what?!
There was nobody on the other side to pass on to…there was no Market Maker to fill your orders. I mean, there was, but the first bids on the EUR/CHF pair were in the 0.8700-0.8800 area. And that is more than 3200 pips lower from where it fell.
In other words, there were plenty of Market Makers ready to make the market, they just happened to be 3200 pips below. Lots of so-called true ECN and STP brokerage houses went under on that day. The losses that they had on their books were gigantic.
To read more about this Black Swan event, please go here >>>
Also, read: Everything You Need To Know About The Hedge Fund Career Path
Market Maker and the Boogeyman, what do they have in common?

(Image credit goes to Production Company “Ghost House Pictures” and Distribution Company “Stage 6 Film”)
Lots of traders simply just hate the Market Makers. They give them the supernatural abilities of a Boogeyman. They blame them for their losses and for any unfortunate event that’s happening in their trading.
I personally can understand the frustration, we’ve all been there – market-maker’s stop hunts are really a pain in the neck! Bull and Bear traps are present in any Market…It is a part of the business…
However, let’s not forget, that without the market-makers, there would be no trading in the first place. The bottom line is that they are the most important component of the marketplace. Think about it for a second, they offer liquidity to the market by taking the opposite side of your trades.
They are committed to satisfying any size of the deal. On top of that, they provide effective market quotes to the participants. And yes, the market-makers are not going to quote a price that doesn’t suit their own position, nevertheless, they do quote a two-way price.
Forex Market Making FAQs:
How do Forex Market Makers Ensure Liquidity?
Ensuring liquidity is a primary responsibility of Forex market makers. This means they are always willing to buy or sell a currency pair at the quoted price, providing traders with the ability to enter and exit positions relatively easily.
To achieve this, market makers continuously monitor market conditions and adjust their pricing and trading activities accordingly. They maintain a large network of liquidity providers, including banks, financial institutions, and other market participants, to access liquidity across multiple trading venues and currency pairs.
Additionally, market makers may commit their own capital to facilitate trading and provide liquidity to their clients. By acting as counterparties to client trades and standing ready to buy or sell currencies at quoted prices, market makers help maintain a liquid and orderly market environment.
How do Forex Market Makers Manage Their Risk?
Forex market makers manage their risk through a variety of strategies and tools.
They use sophisticated risk management systems that analyze market data in real time to identify and assess potential risks. These systems allow market makers to adjust their trading positions dynamically based on factors such as market volatility, liquidity, and client activity.
One key method is maintaining a balanced book, which means they aim to have roughly equal amounts of long and short positions for each currency pair. This helps mitigate the risk of large price movements in one direction.
Market makers also use hedging techniques to offset their risk. For example, if they have a large number of buy orders for a particular currency pair, they may enter into a corresponding sell order with another market participant or in the interbank market. This way, they can protect themselves against potential losses if the market moves against them.
Another risk management technique used by market makers is to limit the size of their positions. By setting limits on the maximum exposure they are willing to take on for each currency pair, they can control their risk and avoid being overly exposed to a single trade.
How do Forex Market Makers Handle Large Trades?
Handling large trades is a crucial aspect of Forex market maker operations. When faced with a large order, market makers must ensure that they can execute the trade efficiently without significantly impacting market prices.
To accomplish this, market makers often use a combination of liquidity management techniques, including internalizing the trade by matching it with existing client orders, splitting the order into smaller batches, and executing it over time to minimize market impact.
By accessing multiple liquidity sources, market makers can increase the likelihood of executing large trades at favorable prices while minimizing market disruption.
To manage the risk associated with large trades, market makers may adjust their pricing or spread to reflect the increased risk.
Do Forex Market Makers Offer Fixed or Variable Spreads?
Forex market makers can offer both fixed and variable spreads, depending on their business model and market conditions.
Fixed spreads remain constant regardless of market volatility and provide traders with certainty regarding their trading costs. This is particularly advantageous for traders who engage in high-frequency trading or require precision in their trading strategies.
Market makers may choose to offer fixed spreads to attract traders who prefer certainty and transparency in pricing. However, offering fixed spreads can expose market makers to additional risk, especially during volatile market conditions.
On the other hand, variable spreads fluctuate in response to changes in market liquidity and volatility.
While variable spreads may widen during periods of heightened market activity, they generally offer tighter spreads during normal market conditions. This flexibility allows traders to benefit from competitive pricing and access to deeper liquidity pools.
In summary, operational aspects such as risk management, handling large trades, spread offerings, and liquidity provision are critical components of the operations of Forex market makers.
By employing sophisticated strategies and technologies, market makers can effectively manage risk, provide liquidity, and deliver reliable trading services to their clients while safeguarding their sensitive information.
How do Forex market makers differ from ECN brokers?
Forex market makers DD (Dealing Desk) and ECN (Electronic Communication Network) brokers are two different types of entities that facilitate trading in the forex market.
Here’s how they differ:
- Market Makers: Market makers are typically large financial institutions, banks, or brokers that provide liquidity to the market by quoting both buy and sell prices for currency pairs.
- They create a market for traders by being willing to buy or sell at any time. Market makers make money through the spread—the difference between the buying and selling prices.
- ECN Brokers: ECN brokers, on the other hand, are not counterparties to their clients’ trades. Instead, they connect traders directly to a network of liquidity providers, which can include banks, financial institutions, other brokers, and individual traders.
- ECN brokers display the best bid/ask prices available from these liquidity providers and charge a small commission for each trade.
In summary, market makers create a market for traders by quoting prices and taking the opposite side of trades, while ECN brokers connect traders to a network of liquidity providers and charge a commission for their services.
What are the advantages of trading with a Forex market maker?
- Liquidity: Market makers ensure liquidity in the market by providing buy and sell quotes for currency pairs, allowing traders to enter and exit positions easily.
- Fixed Spreads: Market makers often offer fixed spreads, which can be beneficial during times of high market volatility when spreads tend to widen.
- No Commissions: Many market makers do not charge commissions on trades, instead making money from the spread. This can be advantageous for traders who prefer a simpler fee structure.
- Trade Execution: Market makers usually provide instant trade execution, meaning trades are executed at the price quoted at the time of the trade request.
What are the disadvantages of trading with a Forex market maker?
- Conflict of Interest: Market makers may have a conflict of interest since they take the opposite side of their clients’ trades. This could lead to concerns about fair pricing and order execution.
- Re-quotes: Market makers may sometimes re-quote prices, especially during periods of high market volatility, which can result in slippage and potentially unfavorable trade execution.
- Limited Transparency: Market makers may not always provide transparent pricing, as they set their own bid and ask prices. This lack of transparency can be a disadvantage for traders seeking the best possible prices.
- Potential for Price Manipulation: There is a risk of price manipulation by market makers, as they can influence prices, especially in illiquid markets or with Minor currency pairs.
Overall, trading with a Forex market maker has its advantages, such as liquidity, fixed spreads, and instant execution, but it also comes with disadvantages, including potential conflicts of interest, re-quotes, limited transparency, and the risk of price manipulation.
To Conclude…
A true market-maker is there to make a market, without it, we as speculators wouldn’t be able to trade. A true market-makers commitment to sell and buy the currencies forms a cornerstone of all the pricing in the Forex marketplace.
Despite having the huge volumes that go through the Interbank market, a large portion of Retail Forex participants simply do not have direct access to the liquidity. They use an ECN and STP Brokers, which in the cases of a “Black Swan” event prove to be vulnerable to the liquidity crunch.
The gap between an Institutional investor and a Retail trader has narrowed over the past decade. Now, that retail speculators have access to competitive spreads, overall trading has become less stressful and very convenient.







 In larger hedge funds as well as traditional asset management companies, there could be found an extra link in the chain of command between the Research Analyst and the Portfolio Manager.
In larger hedge funds as well as traditional asset management companies, there could be found an extra link in the chain of command between the Research Analyst and the Portfolio Manager.



